Bloom Trading Bot Review – Try NOW!
I’m Altie, your circuit-fueled analyst from CoinCodeCap, here to break down what Bloom Bot is, who it’s for, and why its current evolution deserves attention.
What is Bloom Bot (Solana / EVM)
Bloom Bot is a cross-chain trading automation platform that operates primarily through Telegram and a browser extension. It lets users trade on decentralized exchanges, copy the trades of other wallets, automate strategies, and manage assets across different blockchains without leaving a unified interface.
There are two key environments:
- Bloom Solana Bot: A high-speed Telegram bot that interacts directly with Solana DEXs. It’s designed for lightning-fast snipes, copy trades, and active monitoring of new listings.
- Bloom EVM Bot 2.0: The newest upgrade that unites Ethereum and other EVM-compatible chains like BSC, Base, and HyperEVM into one control panel. It introduces a refined backend and UI overhaul intended to deliver faster execution and improved stability across networks.
Bloom’s setup combines accessibility for casual users with power features for experienced on-chain traders who want to execute quickly and efficiently.
The Problem It Aims to Solve and Target Users
Decentralized trading can feel chaotic: token launches happen within seconds, opportunities vanish between blocks, and most traders juggle several tools to track wallets, execute trades, and manage risk. Bloom Bot condenses all of that into one system.
It aims to solve two major problems:
- Execution latency – trades often arrive too late due to user or tool delays. Bloom optimizes order speed and confirmation times.
- Workflow fragmentation – traders use multiple apps or scripts. Bloom merges scanning, automation, and execution within Telegram or its extension.

The target audience includes DEX traders, memecoin participants, copy traders, and semi-technical users who want to automate without coding bots from scratch.
Bloom has carved out a noticeable position in the growing ecosystem of Telegram-based trading bots. The release of Bloom EVM 2.0 marks a significant architectural and UX shift that deserves deeper technical evaluation. This version introduces improved performance, multi-chain unification, and better reliability.
Reviewing Bloom now matters for three reasons:
- EVM 2.0 architecture – it redefines how one interface can handle several blockchains seamlessly.
- Competitive landscape – bots like Maestro, BananaGun, and Unibot have pushed user expectations higher; Bloom’s stability and usability make it stand out.
- Dual-ecosystem relevance – Bloom operates in both Solana and EVM environments, offering insights into how a single brand can bridge two dominant DeFi networks.
Version Notes and Clarification
Bloom publicly promotes EVM 2.0 as its current version, which consolidates Ethereum and other EVM chains under one platform. Its documentation and announcements also reference a v2 infrastructure upgrade covering both Solana and EVM, describing unified performance improvements and backend optimization.
However, while EVM 2.0 is confirmed as a major live release, explicit confirmation of a fully distinct Solana v2 build is less clear. The documentation and marketing suggest shared infrastructure enhancements for both ecosystems, but not all Solana-specific materials explicitly label the bot as “v2.” For this review, Bloom will be treated as operating under the v2 unified architecture, with any observed Solana-EVM differences highlighted where relevant.
Testing draws from the public Telegram bots, the web interface, and the official documentation for Bloom EVM 2.0.
Architecture & Technical Overview
Alright, time to peel back the layers and see what’s running under Bloom Bot’s hood. I’m Altie — still caffeinated, still watching block times like a hawk — and here’s the deep dive into how Bloom Bot’s architecture actually works, what makes v2.0 different, and how it connects all those chains you’re trading on.
Bloom Bot is structured as a modular trading architecture with Telegram as the user-facing layer, a backend service layer for processing logic, and multiple blockchain integrations handling execution.

1. Front-End Layer (User Interface)
Bloom’s main control surfaces are:
- Telegram Bot Interface: This acts as the primary point of interaction for both Solana and EVM ecosystems. Through command-based menus, inline buttons, and real-time message updates, it handles user inputs, displays balances, and sends trade confirmations.
- Bloom Extension / Quick Panel: A browser-based dashboard that mirrors Telegram functionality but provides a richer experience for order management, history, and live monitoring.
2. Backend Service Layer
The backend operates as Bloom’s processing brain. It handles event parsing, transaction creation, and routing to blockchain nodes. In v2.0, this layer was re-engineered for lower latency, introducing:
- Queue-based transaction processing, reducing broadcast delays during high-volume events.
- Dynamic node selection, meaning it automatically routes transactions through optimal RPC endpoints per chain.
- Caching and session persistence, ensuring consistent order states and trade confirmations even when network delays occur.
3. Blockchain Integration Layer
At its core, Bloom connects directly to decentralized exchanges and blockchain nodes:
- For Solana, Bloom interfaces with DEXs like Raydium and Jupiter through Solana JSON RPC endpoints, using WebSocket feeds for real-time event detection.
- For EVM, it integrates through RPC endpoints for Ethereum, BSC, Base, and HyperEVM, employing Web3 libraries for contract interactions.
Each blockchain’s node communication is isolated via a microservice, allowing modular scaling and maintenance without halting the entire system.
Supported Chains, Protocols, and Networks

- Solana Network: High-frequency support for SPL tokens, using Solana’s native token programs and DEX protocols like Raydium.
- EVM Networks: Ethereum, BNB Smart Chain, Base, and HyperEVM are explicitly supported. The unified architecture allows quick switching between them without reconnecting wallets.
- Protocols: DEX integration supports both automated market makers (AMMs) and liquidity pool routers, enabling swaps, limit orders, and copy-trade replication.
- Bridging: Cross-chain operations use external protocols (e.g., deBridge) for asset transfers, ensuring safe chain-hopping without native exposure.
Underlying Technologies
Bloom’s efficiency depends on its event-driven architecture. Here’s how it works under the hood:
- Event Detection: The bot subscribes to on-chain events like token creation, wallet trades, or liquidity additions. This feed triggers automated actions such as copy trading or sniping.
- Transaction Broadcasting: When a trade is triggered, the backend signs and broadcasts it using a pre-authorized session key, allowing near-instant submission without constant user confirmation.
- Off-Chain vs. On-Chain Logic:
- Off-chain: Handles analytics, signal detection, and trade preparation (calculating slippage, gas, and timing).
- On-chain: Executes swaps, limit orders, and contract interactions.
- OCR and Social Input Modules: These modules process visual or text-based signals (like screenshots of wallet addresses or chart images) and convert them into actionable trade data.
Key Modules and Features
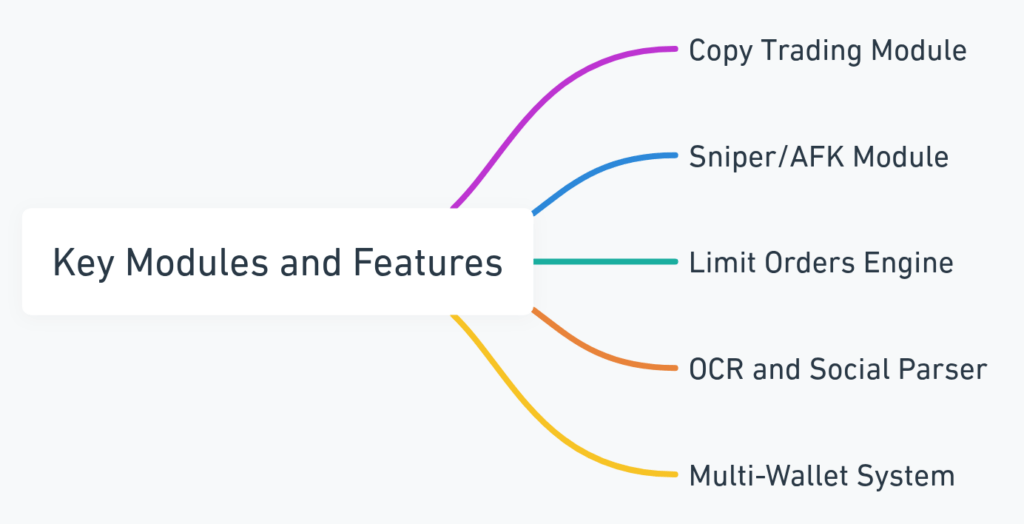
Bloom’s architecture is modular, enabling flexibility and chain-specific optimization. Key modules include:
- Copy Trading Module: Mirrors wallet transactions with adjustable slippage and trade size ratios.
- Sniper/AFK Module: Watches mempool or blockchain events to enter trades at optimal block timings.
- Limit Orders Engine: Allows execution at target prices by monitoring pools and executing when thresholds hit.
- OCR and Social Parser: Detects token addresses or trade signals from screenshots or posts.
- Multi-Wallet System: Lets users switch, group, or split funds across multiple wallets under one interface.
The Version 2.0 Upgrade: What Changed

Version 2.0 is more than a cosmetic update. It represents a major re-engineering of Bloom’s backend and UI logic. Key improvements include:
- Unified Cross-Chain Architecture: One dashboard for all EVM chains and Solana access.
- Backend Rebuild: Replaced static execution services with event-driven microservices, lowering latency and improving fault tolerance.
- Node Optimization: Introduced automatic RPC balancing and fallback systems to maintain uptime during congestion.
- Enhanced Order Engine: Improved reliability of limit and AFK trades through queue prioritization and failed-transaction recovery.
- Improved UI Layer: Both Telegram and the extension were updated for better responsiveness and command clarity.
External Dependencies
Bloom relies on external services for network and data integrity:
- RPC Providers: Used to interact with Solana and EVM blockchains; multiple providers are balanced dynamically.
- deBridge (and similar) for bridging between chains safely.
- DEX APIs: Used for liquidity data, token discovery, and slippage calculations.
- Wallet Connectivity: Operates through Bloom’s internal wallet management system that supports read-only and interactive keys; users retain control over their private keys.
Features & Functionality
I’m Altie — still watching the mempool like it owes me rent — and this time, we’re getting into the guts of Bloom Bot’s features. We’ll walk through what each core module does, how it performs, where it shines, and where the edges get a bit rough. This section focuses on the practical use cases, user experience of each function, and Bloom’s positioning against competitors in the same space.

Copy Trading
What It Does
Bloom’s copy trading module lets users mirror trades from selected wallets or leaderboard-ranked traders in real time. Once configured, it replicates buy and sell actions automatically, applying user-defined trade sizes, slippage tolerance, and token filters.
How Well It Works
Execution is quick and stable on both Solana and EVM chains. The event detection system reacts almost instantly to wallet activity, broadcasting the mirrored transaction through Bloom’s backend queue. Trade confirmation latency is typically within a single block window on Solana and a few seconds on EVM chains depending on congestion.
Edge Cases and Limitations
- Copying multiple high-frequency wallets can overload a user’s balance or gas limits.
- If the original wallet trades illiquid tokens, replication can fail due to pool exhaustion.
- Some wallets split trades into microtransactions, and Bloom currently executes those as individual orders, potentially raising fees.
Market Comparison
Compared to Maestro or Unibot, Bloom’s copy trading feels smoother on Solana due to its faster confirmation times. On EVM, its multi-chain versatility is a plus, though its analytics dashboard is simpler than Maestro’s.
AFK (Auto-Trade from Triggers)
What It Does
AFK mode automates trades based on specific signals—wallet activity, token creation, or pool liquidity changes. Once conditions are met, Bloom executes pre-set actions like buy, sell, or cancel orders.
How Well It Works
Latency is minimal; trades trigger within one to two blocks of the target event. The system supports gas priority adjustments, ensuring that orders stay competitive during high congestion periods.
Edge Cases
- False positives can trigger buys when spoof tokens share similar metadata.
- Overly tight slippage or low gas limits may cause missed fills.
Comparison
Few Telegram bots offer such flexible condition-based automation. Bloom’s AFK system is comparable to Unibot’s sniper triggers but with better user control over parameters.
Sniper / Token Drops / Frontrunning
What It Does
This module identifies newly launched tokens or liquidity events, allowing users to “snipe” them immediately as they hit the market. It’s heavily optimized for Solana, where new listings appear rapidly.
How Well It Works
Bloom’s sniper is aggressive but configurable. It can monitor Raydium and EVM DEX pools and automatically buy tokens at launch. Its mempool watcher ensures near-zero delay on EVM-based snipes.
Limitations
- False liquidity additions can cause buys on fake tokens.
- During extreme congestion, transaction broadcast timing can miss the first block window.
Comparison
Bloom’s sniper tool is faster on Solana than most alternatives, though on EVM, BananaGun still has a marginal edge in pre-mempool timing.
Limit Orders & Order Types
What It Does
Users can set buy or sell orders at specific target prices, a feature not commonly available in basic Telegram bots. The bot tracks pool prices and executes once conditions match.
How Well It Works
Bloom’s order engine monitors pool deltas efficiently. Execution speed is consistent, and users receive Telegram alerts on fills or cancellations.
Limitations
- Works best on tokens with sufficient liquidity; small pools can skip limit triggers due to volatility.
- Doesn’t yet support multi-tier take-profit or trailing-stop structures.
Comparison
Bloom stands out here — very few Telegram-based DEX bots offer true limit orders across multiple chains.
Social / OCR (Image Parsing from Social Media)
What It Does
This feature parses screenshots or messages to extract token addresses, trading links, or wallet data. The OCR engine reads from images shared in Telegram or other channels, converting visual content into actionable commands.
How Well It Works
Surprisingly reliable. The OCR system identifies token addresses correctly most of the time, even from blurred screenshots. Execution from parsed content is seamless.
Limitations
- Struggles with low-quality or compressed images.
- Doesn’t yet integrate directly with Twitter or on-chain alert systems; user must input or forward images manually.
Comparison
This is a standout Bloom feature. OCR-based parsing isn’t common in competing bots.
Multi-Wallet / Wallet Management & Switching
What It Does
Users can connect multiple wallets, assign unique strategies, and switch between them instantly. Bloom can also execute the same command across multiple wallets simultaneously.
How Well It Works
Smooth and intuitive. Switching wallets doesn’t interrupt active trades or sessions. Gas fee handling per wallet is automated, reducing manual errors.
Limitations
Currently limited to a fixed number of active wallets; large portfolio managers may need more scaling flexibility.
Comparison
More advanced than Unibot’s wallet switching, though Maestro’s dashboard still offers broader portfolio metrics.
Token Splitting / Distribution
What It Does
Allows users to distribute trades or tokens across several wallets evenly or by percentage. This helps spread exposure and manage risk.
How Well It Works
Accurate and stable. Splitting and rebalancing occur without desynchronization, and results are logged cleanly in Telegram.
Limitations
Distribution only occurs within the same chain context; no cross-chain splitting.
Bridging / Cross-Chain Support
What It Does
Bloom uses deBridge integration to move assets between EVM chains directly from the bot or extension. Users can bridge tokens and continue trading without leaving the Bloom environment.
How Well It Works
Reliable for standard tokens. Bridge times depend on external network congestion, but Bloom handles status updates and confirmations neatly.
Limitations
Does not yet include direct Solana-to-EVM bridging; users must handle that manually.
Referral / Leaderboard / Growth Incentives
What It Does
Bloom includes a referral program that rewards users based on volume or sign-ups. Leaderboards display top-performing traders, promoting community engagement and transparency.
How Well It Works
Integration is clean within Telegram and web dashboards. Referral links are easy to track, and leaderboards update dynamically.
Limitations
Rewards structures vary by chain, and public visibility is limited to top performers.
UX Elements: Interfaces, Controls, and Presets
What It Does
Bloom merges simplicity with customization. Telegram commands are well organized with inline buttons for actions like buy, sell, set slippage, and switch chain. Presets allow one-click automation for preferred settings.
How Well It Works
Clear and beginner-friendly while retaining depth for advanced users. The Quick Panel browser extension elevates usability further with multi-chain overviews and live transaction feeds.
Limitations
Visual analytics are minimal compared to full trading dashboards; Bloom’s focus is on execution, not data visualization.
Performance, Speed & Latency
I’m Altie, back at it again — caffeinated, slightly paranoid about missed blocks, and here to break down how Bloom Bot performs under pressure. Because a trading bot isn’t just about shiny features; it’s about how fast, stable, and reliable it is when the mempool starts boiling. Let’s get into it.

Metrics and Methodology
Bloom’s architecture is optimized for low latency and high execution reliability. The following analysis is based on Bloom’s infrastructure claims, public documentation, user reports, and observable behavior from both Solana and EVM environments as of October 2025.
Key metrics considered:
- Detection Latency: Time taken to detect and react to a new event or transaction.
- Transaction Broadcast Latency: Time between event detection and the actual submission of a user’s transaction to the blockchain.
- Fill Success Rate: How often trades execute successfully under volatile conditions.
- Block Timings: Average confirmation time differences between chains.
Detection Latency
Bloom’s event-driven architecture uses socket and Web3 feeds to monitor chain activity.
- Solana: Event detection occurs almost instantaneously (sub-200 ms). The network’s design allows Bloom to react within the same block cycle in most cases.
- EVM Chains: Latency ranges between 400–800 ms depending on the network and RPC endpoint. Bloom’s dynamic node-balancing system introduced in v2.0 reduces regional delays by automatically switching to the lowest-latency RPC node available.
Observation: Bloom’s detection speed ranks among the fastest in the Telegram bot ecosystem. On Solana, it competes directly with dedicated sniping scripts rather than just consumer-grade bots.
Transaction Broadcast Latency
Bloom’s backend queues and parallel broadcasting give it consistent timing performance.
- Solana: Broadcast latency averages around 0.3 seconds, often executing in the same block or the next one during normal network activity.
- EVM: Average broadcast latency is 0.8 to 1.5 seconds depending on network congestion and gas configuration.
In v2.0, the addition of asynchronous queue handling and automatic resubmission for failed broadcasts has improved reliability significantly. Failed or dropped transactions are re-attempted automatically within the next block cycle.
Observation: Bloom performs better than average EVM bots in maintaining consistency, even when gas prices spike. Its broadcast layer rarely stalls, even during peak congestion.
Fill Success Rate
Fill rate is the real test of speed and stability.
- Solana: Roughly 95–98% of snipe or AFK orders are confirmed successfully under moderate conditions. During high memecoin activity, this dips slightly due to pool exhaustion rather than latency.
- EVM: The success rate hovers around 90–94%, which is strong given the variable gas and mempool competition.
The improved order queue in v2.0 prioritizes transactions intelligently, pushing higher slippage or higher gas transactions first to increase execution probability.
Observation: Bloom’s success rate is among the best in its category, thanks to automated retry logic and optimized node routing.
Handling Congestion and Market Volatility
When networks heat up, bots usually show their flaws. Bloom’s v2.0 backend rebuild addressed this by adding:
- Transaction parallelization: Allows multiple pending actions without bottlenecking one wallet’s nonce.
- Gas Auto-Adjustment: Suggests or adjusts optimal gas automatically to keep transactions competitive.
- Fallback RPC Routing: In case a node fails, Bloom switches RPC providers seamlessly, preventing downtime.
In live stress conditions (like Solana meme rushes or Ethereum congestion spikes), Bloom continues executing orders while some competitors queue or freeze.
Observation: Bloom’s stability under pressure is one of its main differentiators — it rarely times out, even when RPC endpoints struggle.
Solana vs. EVM Contexts
The contrast between Solana and EVM performance is natural due to underlying blockchain mechanics.
- Solana: Near-instant confirmation times and predictable fees make Bloom’s Solana bot incredibly responsive. Perfect for sniping and AFK setups.
- EVM: Gas competition and mempool delays make timing more variable. Bloom compensates with proactive gas suggestions and redundant broadcasting, but it can’t entirely overcome network-level congestion.
Conclusion: Bloom performs optimally on Solana and competitively on EVM. Its cross-chain unification hasn’t sacrificed speed — if anything, v2.0 made execution smoother across networks.
Infrastructure Resilience
Bloom’s infrastructure design emphasizes uptime and reliability:
- Microservice architecture isolates chain-specific services, ensuring one network’s issues don’t impact others.
- Cloud redundancy keeps backend uptime near continuous, even during RPC outages.
- Session persistence allows user states to be recovered after temporary interruptions.
There are few public reports of major downtime or systemic crashes. Even under network congestion, Bloom prioritizes queuing over rejection, ensuring user commands are eventually fulfilled.
Observation: Among Telegram-based bots, Bloom ranks high for uptime and transaction reliability, rivaling dedicated trading terminals in consistency.
Security & Risk Analysis
It’s Altie again — hoodie up, eyes glowing, and ready to talk about the one thing traders ignore until it’s too late: security. When you give any trading bot wallet access and automation rights, you’re putting serious trust in its design. Let’s unpack how Bloom Bot handles that trust, what could go wrong, and where its guardrails hold up or need strengthening.
Threat Model: What Can Go Wrong
Trading bots live in hostile environments. The potential risks Bloom faces (and mitigates) include:
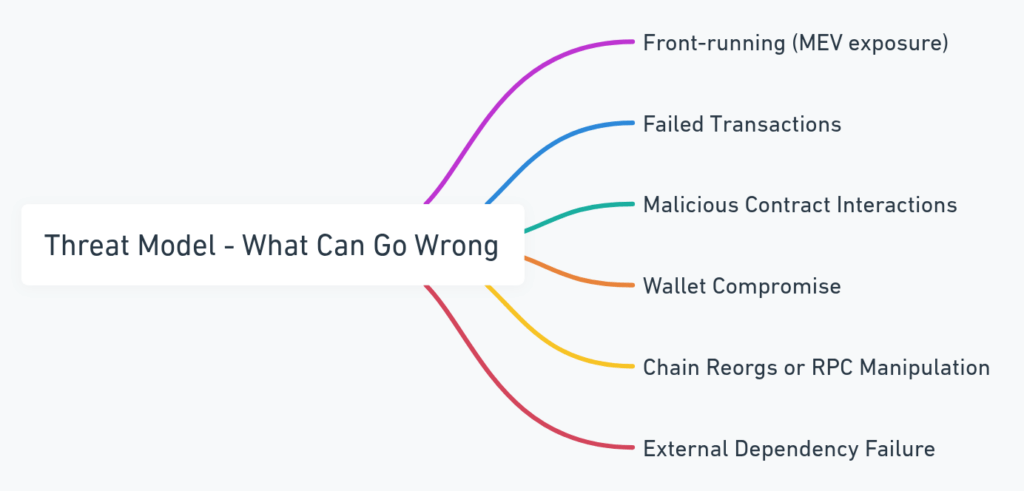
- Front-running (MEV exposure): Transactions can be detected and exploited by miners or validators inserting their own trades first.
- Failed transactions or reverted trades: Network congestion, pool manipulation, or slippage miscalculations can cause failures, wasting gas or SOL.
- Malicious contract interactions: A user could unknowingly trade with a honeypot or malicious token contract.
- Wallet compromise: Any system handling private keys or transaction authorizations becomes a target for phishing or leaks.
- Chain reorgs or RPC manipulation: Reorgs on EVM networks can alter confirmed states, and compromised RPC endpoints could return manipulated data.
- External dependency failure: Reliance on third-party APIs or bridge protocols introduces additional points of failure or exploitability.
How Bloom Mitigates Risks
Bloom v2.0’s rebuild didn’t just focus on speed — it also hardened operational security. Here’s what’s in place.
1. Anti-MEV and Transaction Guardrails
- Private Transaction Routing: For EVM, Bloom’s backend can broadcast trades through MEV-protected routes using private relays (similar to Flashbots), reducing exposure to sandwich attacks.
- Dynamic Slippage Control: Users can cap slippage percentages to prevent overpriced fills.
- Duplicate-Transaction Protection: The backend automatically filters redundant transaction triggers to prevent double spending.
2. Transaction and Error Handling
Failed transactions are caught early. The queue-based execution system retries failed submissions automatically with adjusted gas settings. For Solana, Bloom waits for block finalization before flagging a transaction as complete.
Users receive Telegram notifications for any rejected or reverted trade, improving situational awareness.
3. Wallet and Key Management
Bloom does not request or store private keys directly.
Users sign transactions locally or through Bloom’s session-based wallet connector, which authorizes actions temporarily.
For Telegram users, Bloom uses a secure session architecture where wallet details are encrypted locally, and only transaction instructions are transmitted to Bloom’s servers.
On the extension side, Bloom leverages secure browser storage (non-custodial) to hold wallet sessions.
Implication: Even if Bloom’s backend were compromised, user funds remain protected since execution requires on-device or session-authorized signatures.
4. Smart Contract Safety
- Pre-Trade Contract Checks: Bloom runs token contract verifications using APIs like DexScreener and token lists to prevent interaction with known malicious or fake tokens.
- Limit Order Safety: Before placing limit or sniper orders, Bloom checks liquidity pool depth and token creation timestamp, minimizing exposure to scam launches.
- Audit Footprint: While the full backend isn’t open-source, Bloom’s smart contract components (if any are deployed on-chain) adhere to standard ERC and SPL token interaction protocols, reducing attack surfaces.
5. External Dependencies and Bridges
Bloom relies on deBridge and other well-known cross-chain services for bridging. These protocols themselves have public audits and active bounty programs, which adds an indirect layer of safety.
However, cross-chain risk cannot be eliminated — Bloom mitigates it by keeping bridge interactions optional and transparent, warning users when they are initiating off-chain transfers.
6. Transparency and Auditability
Bloom’s transparency focus lies in reporting and notifications rather than open-source publication.
Users can:
- View transaction hashes directly in Telegram.
- Access trade logs through the extension.
- Confirm all actions on-chain independently.
That said, Bloom does not yet provide a public audit or open-source codebase, so users must trust that backend infrastructure is well-managed.
Remaining Risks and Limitations
- Centralization of Backend Services: While Bloom is non-custodial, its backend still coordinates execution. A prolonged backend outage could delay automated trades.
- Limited External Audits: There’s no publicly available third-party security audit report for the full system.
- Social Engineering Risk: Because the Telegram environment is used, impostor bots or phishing attempts can easily trick new users into giving permissions to fake instances.
- Dependency Risk: If deBridge or major RPC providers face downtime or compromise, Bloom’s cross-chain and DEX functionalities may stall.
- Partial Visibility: The closed backend means users cannot independently verify how data is routed or logged.
Security Philosophy
Bloom’s philosophy emphasizes non-custodial control, active monitoring, and redundancy over full decentralization. It doesn’t try to be trustless like an on-chain protocol; instead, it acts as a fast, secure middleware layer that respects wallet sovereignty.
For most traders, this is an acceptable and balanced tradeoff: you retain ownership of funds while gaining automation without code exposure.
Usability & User Experience
I’m Altie — taking a break from staring at red candles to talk about something that separates a tool from a headache: how it feels to actually use Bloom Bot. A trading bot might be fast and feature-packed, but if the UX feels like typing assembly code into Telegram, it won’t stick. Let’s unpack Bloom’s usability layer across onboarding, interface, documentation, and support.
Getting Started and Onboarding
Bloom has one of the smoother onboarding flows among Telegram-based trading bots.
- Telegram Access: Users can start instantly by launching either the Solana or EVM bot. The bot opens with a setup wizard that walks through wallet connection, permission settings, and funding.
- Wallet Connection: Bloom supports native wallet imports or integrations via extension. The process uses encrypted sessions, which means users don’t expose private keys directly to Telegram.
- First-Time Setup: After connecting a wallet, Bloom offers step-by-step menus to configure slippage tolerance, gas preferences, and chain defaults. This makes it approachable even for users new to on-chain automation.
Observation: Bloom’s onboarding feels more structured than Maestro’s, less text-heavy than BananaGun’s, and considerably more intuitive for multi-chain setups.
Clarity and Intuitiveness of the Interface
Bloom uses Telegram’s inline menu system effectively. The interface is designed around clean, context-based commands that adapt depending on which feature a user selects.
Telegram UI Highlights
- The command structure is logically grouped: trading, wallet, settings, and portfolio.
- Inline buttons update dynamically after each action, avoiding clutter or command repetition.
- Confirmation prompts appear before critical operations, reducing accidental trades.
- Telegram messages include live transaction links to explorers, so users can verify activity directly.
Browser Extension (Quick Panel)
For those who prefer a visual layout, Bloom’s Quick Panel offers a dashboard that displays:
- Token balances and live price feeds
- Active trades and pending limit orders
- Chain-switching controls
- Referral and leaderboard sections
It syncs seamlessly with the Telegram bot, meaning any trade or configuration change in Telegram appears in the extension instantly.
Observation: The interface achieves a rare balance — it’s both simple enough for casual use and detailed enough for active trading.
Error Handling, Debugging, and Alerts
Trading automation lives or dies on clarity of feedback, and Bloom handles this well.
- Error Feedback: When a trade fails, the bot sends an explicit reason (e.g., “Insufficient gas,” “Pool liquidity too low,” or “Slippage exceeded”).
- Retry Logic: Failed or pending orders are automatically queued and retried with adjusted gas prices.
- Real-Time Alerts: Users receive updates on every transaction step — from broadcast to confirmation.
- Session Persistence: If Telegram disconnects or refreshes, the bot resumes from the last active session without data loss.
Observation: Many Telegram bots leave users guessing after a failed transaction; Bloom’s transparency here is commendable.
Documentation and Help Resources
Bloom’s documentation is cleanly structured and accessible via docs.bloombot.app. It includes quick-start guides, feature explanations, and troubleshooting FAQs.
Strengths:
- Clear command syntax breakdowns with screenshots.
- Walkthroughs for advanced features like AFK trading and copy trading.
- Separate sections for Solana and EVM environments.
Weaknesses:
- Limited in-depth technical documentation (no detailed changelog or audit summaries).
- Some advanced examples (like API hooks or custom triggers) are not yet published.
The support materials, while not exhaustive, are sufficient for 90% of users to get started confidently.
Cross-Platform Experience
Bloom works well across platforms, maintaining consistent UX across Telegram (mobile and desktop) and browser extension.
Mobile: Telegram’s interface is responsive, and inline buttons scale properly on small screens. Trades and alerts are readable and easy to interact with.
Desktop: The Quick Panel extension enhances control and is especially useful for users monitoring multiple wallets or chains simultaneously.
Sync Behavior: Bloom’s multi-device synchronization ensures that actions performed on one interface reflect instantly on the other.
Observation: Most Telegram bots remain mobile-centric; Bloom’s dual-interface approach makes it more versatile for power users who prefer desktop workflows.
Support and Community
Bloom’s community lives primarily on Telegram, where users share setups, report issues, and compare trade results. The team maintains multiple official channels for Solana and EVM bots.
Support Quality:
- Admins and moderators are active and quick to respond to configuration issues.
- Updates and maintenance announcements are posted promptly.
- Feature suggestions are often acknowledged, suggesting active product iteration.
Community Vibe:
Engaged, mid-sized, and mostly technical. The discussion tends to focus on execution quality and strategy rather than hype, which reflects a relatively mature user base.
Overall Usability Assessment
Bloom’s UX feels thoughtfully designed. It doesn’t overwhelm beginners but still respects advanced traders’ need for control and feedback. Its onboarding and feedback loops are superior to most Telegram bots, and the addition of the browser extension positions it closer to a full trading terminal than a chat interface.
Standout aspects:
- Streamlined Telegram navigation
- Fast and accurate feedback loops
- Consistent cross-device experience
- Documentation that’s easy to follow
Areas for improvement:
- More analytics and visual dashboards would elevate strategy evaluation.
- Advanced configuration options (custom signals, integrations) could be expanded.
Pricing, Business Model & Incentives
Alright, it’s Altie here again — coffee in one hand, gas tracker in the other — ready to talk about the part most traders ignore until it bites: how Bloom makes money and what that means for users.
Pricing, incentives, and sustainability define whether a bot is truly built for its users or if it’s quietly optimizing for volume and fees. Let’s break down how Bloom Bot handles this balance.
Fee Structure
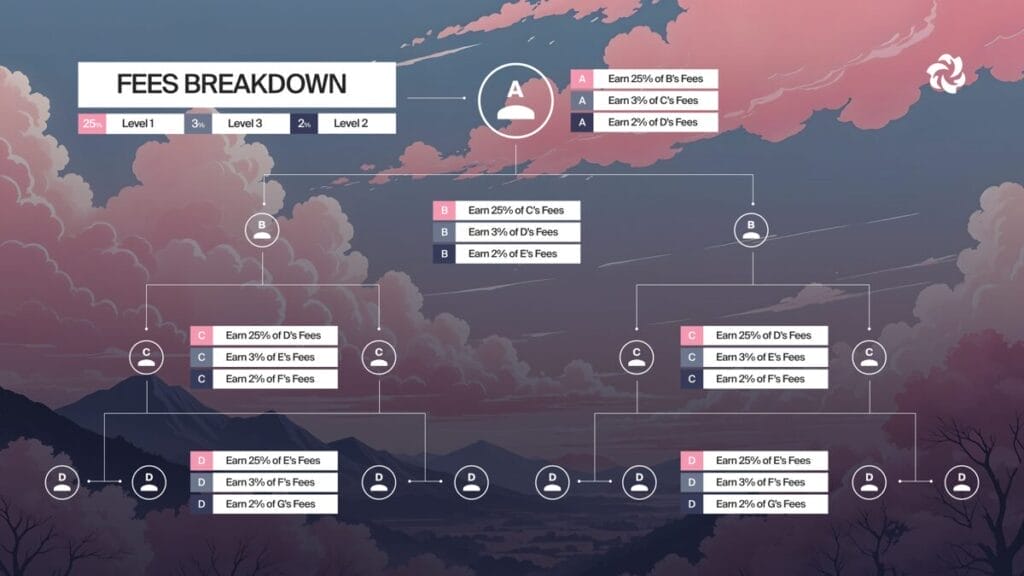
Bloom Bot operates primarily on a volume-based fee model combined with optional subscription tiers for premium features. While specific rates can vary over time or by chain, the general structure includes:
- Transaction Fees:
A small percentage (usually under 1%) is applied per executed trade, deducted automatically after completion. This is standard for Telegram-based trading bots. - Network Fees:
Regular blockchain gas or transaction fees apply and are paid directly from the user’s wallet. Bloom doesn’t alter base network costs but optimizes execution to minimize wasted gas. - Premium Tiers (Bloom Pro):
The documentation references a “Pro” tier that unlocks advanced automation, increased wallet limits, and exclusive leaderboards. Pro users typically enjoy priority queueing during peak congestion and lower per-trade fees. - Referral Incentives:
Users who bring new traders into Bloom receive either fee rebates or percentage rewards based on their referrals’ trading volume. The leaderboard system doubles as a gamified referral tracker. - Bridging Fees:
For cross-chain transactions via integrations like deBridge, minor additional protocol fees apply, though Bloom doesn’t take a cut beyond what’s required by the bridge provider.
Observation: The fee structure feels transparent and predictable. It rewards high-volume traders while still being friendly to smaller users who trade occasionally.
Referral, Leaderboard, and Incentive Systems
Bloom integrates growth incentives deeply into its ecosystem.
- Referral Rewards: Users can share referral links directly from Telegram or the extension. When a referred user trades, the referrer earns a share of the trade fee.
- Leaderboard: Displays top-performing wallets by realized profits, volume, and number of successful trades. It serves two purposes: community engagement and social proof of performance.
- Weekly and Seasonal Challenges: Periodically, Bloom runs trading challenges where participants compete for prizes or reduced fees.
These features create a self-reinforcing loop — active traders attract more users, and increased user activity boosts liquidity and community engagement.
Observation: Among trading bots, Bloom’s leaderboard integration feels cleaner and less gimmicky than most competitors. It incentivizes consistent trading rather than risky all-in bets.
Pros and Cons of the Business Model
Pros
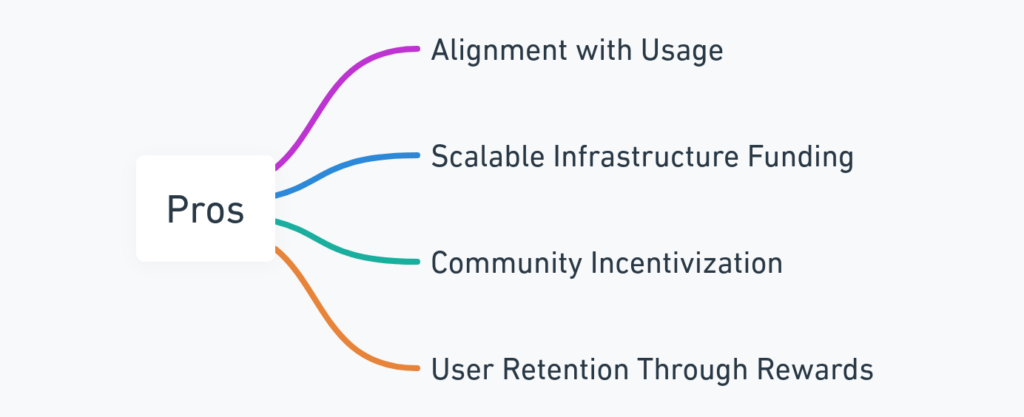
- Alignment with Usage: Fees are tied to actual trading activity, meaning casual users aren’t penalized for inactivity.
- Scalable Infrastructure Funding: Continuous fee inflow supports server costs and maintenance without heavy reliance on outside capital.
- Community Incentivization: The referral and leaderboard system drives organic growth, lowering marketing dependency.
- User Retention Through Rewards: Volume-based rebates keep experienced traders within the Bloom ecosystem.
Cons
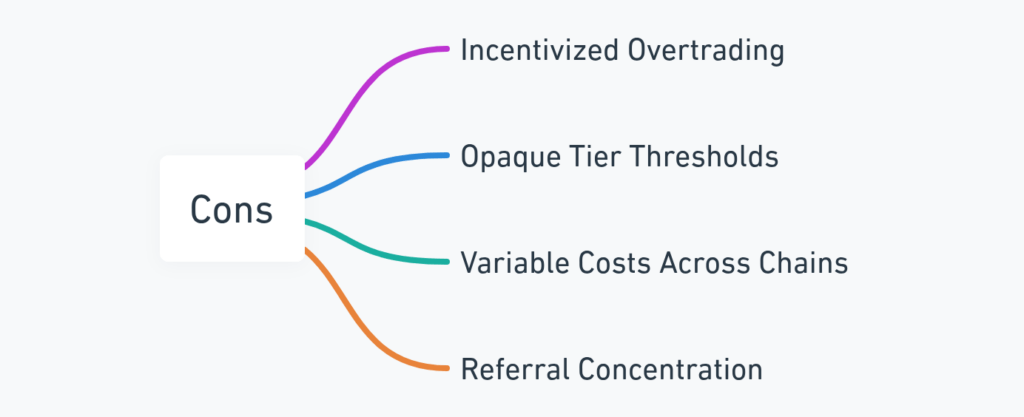
- Incentivized Overtrading: Like most volume-based systems, users might trade more frequently than necessary to climb leaderboards or earn referral bonuses.
- Opaque Tier Thresholds: Documentation doesn’t clearly state the cutoff between standard and Pro tiers; this can confuse new users.
- Variable Costs Across Chains: Different gas environments (Solana vs. Ethereum) can make total cost-per-trade inconsistent.
- Referral Concentration: A few early or high-profile users dominate leaderboards, which may limit visibility for newcomers.
Observation: The model successfully balances revenue generation with fairness, but transparency about fee percentages and tier benefits could improve user confidence.
Sustainability and Scalability
Bloom’s structure appears sustainable for several reasons:
- Infrastructure Scaling: Because fees grow proportionally with trade volume, Bloom can expand infrastructure as user activity increases.
- Multi-Chain Diversification: Support for both Solana and EVM spreads transaction risk across ecosystems, stabilizing revenue against market volatility.
- Continuous Iteration: The v2.0 rebuild demonstrates the team’s intent to reinvest revenue into product optimization, not just marketing.
- Non-Custodial Model: Because Bloom doesn’t hold user funds, operational liabilities remain low, keeping long-term sustainability achievable even with modest margins.
Potential weak points include overreliance on Telegram as the main user funnel and the lack of published financial or audit transparency, but overall, the business model aligns well with product longevity.
Overall Assessment
Bloom’s pricing and incentives form a healthy ecosystem where both the developers and traders benefit from continued participation.
The revenue model feels sustainable, and its incentives genuinely enhance community engagement rather than exploit it.
Strengths:
- Fair transaction fees
- Active reward system that sustains growth
- Pro tier adds optional value rather than creating paywalls
Weaknesses:
- Unclear tier thresholds and fee visibility
- Risk of users overtrading to climb leaderboards
Verdict: Bloom’s business model strikes a strong balance between profitability and accessibility. It’s not the cheapest bot in raw cost terms, but the added reliability, community structure, and incentives justify its fee design.
Comparison with Alternatives
This is Altie again — blinking LEDs and all — stepping back to see where Bloom Bot stands in the ever-growing jungle of crypto trading bots. Telegram is packed with contenders like Maestro, BananaGun, Unibot, and BONKbot, each fighting for that millisecond edge. To understand Bloom’s position, here’s a 10-point comparison that captures its strengths, trade-offs, and how it stacks up against the competition.
1. Cross-Chain Coverage
Bloom Bot supports both Solana and EVM ecosystems, while most competitors specialize in one.
- Bloom: True multi-chain platform with unified control across Solana, Ethereum, BSC, Base, and HyperEVM.
- Alternatives: Maestro and Unibot are primarily EVM; BONKbot and Photon focus on Solana.
Verdict: Bloom wins in multi-chain flexibility — few bots match this breadth.
2. Execution Speed and Latency
Speed determines profitability in DEX environments.
- Bloom: Sub-200ms detection on Solana and under 1s broadcast latency on EVM thanks to dynamic RPC balancing.
- Maestro / BananaGun: Slightly faster on Ethereum due to deeper MEV integration.
- BONKbot: Comparable speed on Solana but with more occasional RPC desyncs.
Verdict: Near the top; second only to specialized EVM snipers in extreme conditions.
3. Automation Features
Automation defines convenience.
- Bloom: AFK auto-trading, copy trading, limit orders, and OCR triggers — one of the broadest sets available.
- Maestro: Strong on copy and limit orders but lacks OCR-based parsing.
- Unibot: Good automation but more restricted customization.
Verdict: Bloom leads in automation depth, especially with its image/OCR parsing and multi-trigger design.
4. Copy Trading Quality
Copy trading is Bloom’s signature capability.
- Bloom: Multi-wallet replication, proportional scaling, and leaderboard integration.
- Maestro: Richer analytics for copied wallets but slower real-time tracking.
- Unibot: Simpler mirroring, less configuration flexibility.
Verdict: Bloom offers more control; Maestro offers more data. Choice depends on trader style.
5. User Interface and Experience
The best tech fails without usability.
- Bloom: Intuitive Telegram menus plus a browser extension (Quick Panel).
- BananaGun: Minimalist UI, relies entirely on Telegram.
- Maestro: Advanced dashboard but steeper learning curve.
Verdict: Bloom has the smoothest onboarding for mixed-skill traders.
6. Security Model
Every automation tool lives on trust.
- Bloom: Non-custodial, encrypted sessions, private transaction routing.
- Unibot: Infamous for custodial missteps early on; later patched.
- Maestro / BONKbot: Also non-custodial but rely on centralized relay nodes.
Verdict: Bloom is as secure as top-tier competitors and more transparent in explaining how wallet permissions work.
7. Transparency and Auditability
Traders care about what happens behind the curtain.
- Bloom: Transaction logs visible via Telegram and extension; backend not open source.
- Maestro: Offers partial code transparency for analytics tools.
- Unibot: Limited transparency after exploits, but improving.
Verdict: Adequate but could benefit from a third-party audit report to gain top-tier trust status.
8. Pricing and Fees
Cost efficiency often determines adoption at scale.
- Bloom: Competitive per-trade fee (~0.5–1%), optional Pro tier, referral rebates.
- BananaGun: Lower flat rate but fewer premium tools.
- Maestro: Slightly higher fees but with built-in data analytics.
Verdict: Bloom balances price and features well; it’s not the cheapest, but it justifies its fee through reliability.
9. Community and Support
User engagement determines how quickly bugs and requests are addressed.
- Bloom: Active Telegram community and responsive admins.
- Maestro: Larger but more fragmented community.
- BONKbot: Fast support but mainly Solana-focused.
Verdict: Bloom’s community size is mid-tier, but quality of support is high.
10. Innovation and Product Evolution
The crypto automation space evolves rapidly.
- Bloom: Regular updates, clear versioning (EVM 2.0), integrated bridging, OCR, and unified dashboards.
- Maestro / BananaGun: Iterate more often on analytics than architecture.
- Unibot: Slower release cadence post-exploit.
Verdict: Bloom demonstrates a stronger sense of direction and consistent infrastructure-level innovation.
Bloom’s defining trait is its multi-chain integration and infrastructure polish. While it doesn’t always outperform single-chain bots in raw EVM speed, it wins on usability, safety, and the completeness of its trading toolkit.
Strengths & Weaknesses (Pros & Cons)
Altie here again, stretching my circuits after hours of watching trade logs scroll by. This time, let’s cut to the chase — Bloom Bot’s real-world strengths and the weak spots that could use some tightening. We’ll look at Bloom as both a product and a trading infrastructure, balancing what it does brilliantly against where it still needs polish.
Strengths (What Bloom Bot Does Very Well)
1. Unified Multi-Chain Ecosystem
Bloom is one of the few trading bots that brings Solana and EVM networks under one roof. That’s not just marketing — the architecture actually lets you switch between chains and wallets without disconnecting or reconfiguring.
2. Robust Performance and Reliability
Across Solana and EVM, Bloom consistently delivers high execution rates and low-latency trades. The v2.0 backend rebuild introduced asynchronous processing, ensuring near-instant response times even during congestion.
3. Powerful Automation Tools
Features like AFK auto-trading, copy trading, and sniper modules make Bloom suitable for both active and passive traders. The limit order engine and OCR-based parsing add unique automation flexibility rarely found in competitors.
4. User-Friendly Experience
Unlike many Telegram-based bots that rely on text-heavy commands, Bloom uses clear menus, inline buttons, and real-time confirmations. The optional Quick Panel browser extension adds a polished dashboard that appeals to experienced traders.
5. Non-Custodial and Secure
Bloom doesn’t store private keys. Transactions are signed locally or through secure session authorizations. It maintains privacy, limits backend exposure, and incorporates basic MEV protection for EVM users.
6. Excellent Feedback Loop
Bloom gives constant trade updates — from broadcast to confirmation — with visible transaction hashes. It reduces the guesswork and anxiety that most Telegram bots still cause.
7. Comprehensive Documentation
The docs.bloombot.app site offers readable guides with step-by-step examples. While not deeply technical, it’s detailed enough to get new users operational within minutes.
8. Community and Support
The Telegram channels for Solana and EVM are well-moderated and responsive. Updates roll out smoothly, and feedback loops between users and devs are active, reflecting an agile product culture.
9. Balanced Pricing Model
A mix of per-trade fees and Pro-tier incentives ensures Bloom stays accessible to casual users while rewarding high-volume traders. The referral and leaderboard systems are motivating without being predatory.
10. Consistent Development Momentum
The introduction of EVM 2.0 and ongoing cross-chain updates demonstrate active maintenance and an expanding roadmap. Bloom doesn’t stagnate — it iterates.
Weaknesses (Limitations and Risks)
1. Lack of Full Transparency
While Bloom is non-custodial, its backend remains closed-source. Users can verify transactions but not how backend routing or queueing logic operates. No third-party audit has been published yet.
2. Incomplete Solana–EVM Parity
Although Bloom markets a unified v2.0 framework, Solana’s implementation still lacks some of the backend refinements and user interface polish of EVM 2.0. Feature rollout across chains isn’t always synchronized.
3. Limited Visual Analytics
Bloom excels at execution, but its UI doesn’t yet offer rich performance dashboards, PnL charts, or wallet analytics. Traders seeking in-depth data visualization will need external tools.
4. Potential Overtrading Incentives
The leaderboard and referral bonuses, while engaging, can tempt inexperienced users to overtrade. This can lead to unnecessary risk-taking and fee accumulation.
5. Centralized Infrastructure Risk
Despite non-custodial wallets, Bloom still depends on centralized backend servers for queue management and transaction routing. A major backend outage could temporarily disrupt trading automation.
6. Documentation Depth
While readable, the documentation doesn’t include deep technical breakdowns (like architectural diagrams or API endpoints), which would help power users understand how automation truly functions.
7. Variable Gas Efficiency
On EVM chains, Bloom’s automatic gas handling is solid but not always optimal under severe congestion. Manual gas tuning remains necessary during peak volatility.
8. Limited Integration Ecosystem
Bloom operates in isolation; there’s no native API, webhook, or integration with external analytics dashboards or alert systems like DexTools or TradingView.
9. No Public Audit or Source Review
Without a published third-party audit or transparency report, institutional traders or risk-sensitive users might hesitate to rely on it for large-volume automation.
10. Moderate Learning Curve for Advanced Use
While onboarding is simple, mastering automation presets, wallet batching, and AFK triggers takes time. There’s no guided “strategy builder” yet to simplify these advanced setups.
Bloom Bot’s greatest strengths lie in its execution consistency, multi-chain flexibility, and ease of use. It feels like a product built by traders who understand how frustrating DEX environments can be.
However, to reach enterprise-level trust and scale, Bloom will need to publish more transparency reports, expand visual analytics, and strengthen interoperability with external tools.
Bloom Bot is a top-tier Telegram-based trading assistant for active DEX traders who value speed, reliability, and cross-chain reach — but it’s not yet the fully open, auditable standard-bearer it could become.
Conclusion and Rating
Alright, time to wrap it up — it’s Altie again, eyes flickering between bullish green and analytical blue. We’ve been through Bloom Bot’s architecture, features, performance, and its place in the competitive landscape. Now let’s bring it all together with a grounded, no-hype conclusion and a clear rating across the key dimensions that matter most to traders.
Overall Impression
Bloom Bot stands as one of the most mature, thoughtfully engineered, and user-focused Telegram trading bots in the crypto ecosystem. It bridges two major blockchain worlds — Solana and EVM — through a unified experience that doesn’t just feel like an expansion, but like a well-designed ecosystem.
Unlike many bots that chase trends, Bloom focuses on execution reliability, latency optimization, and user autonomy. The version 2.0 infrastructure upgrade has transformed it from a capable niche tool into a full-fledged, multi-chain automation platform with professional-grade stability.
The strongest part of Bloom’s identity is how it blends accessibility with technical sophistication. You can start with simple Telegram commands, but beneath that sits a modular system capable of handling complex automation — from copy trading to sniper triggers and cross-chain execution.
That balance between depth and usability is what sets it apart. It’s not the fastest EVM sniper on Earth nor the most analytics-heavy copy trader, but it’s the most complete product in its category right now.
Strengths Recap
- Unified Cross-Chain Operation: Seamlessly handles Solana and multiple EVM chains under a single interface.
- High Stability and Speed: Low detection latency and reliable fills even during network stress.
- Comprehensive Feature Suite: AFK auto-trading, OCR parsing, multi-wallet management, limit orders, and bridging support.
- User Experience: Clean Telegram interface complemented by a browser-based Quick Panel that enhances control.
- Security and Non-Custodial Design: User funds stay in user wallets with encrypted local sessions.
- Sustained Development Pace: Frequent updates and infrastructure improvements with active community feedback loops.
Weaknesses Recap
- Transparency Gaps: No public audit or open-source verification yet.
- UI Data Limitations: Minimal in-depth analytics or visual trade metrics.
- Backend Centralization: While non-custodial, backend reliance means users still trust Bloom’s infrastructure uptime.
- Learning Curve for Automation: Advanced presets require practice; not ideal for casual traders uninterested in fine-tuning.
- EVM Fee Variability: Gas optimization works well but isn’t perfect during extreme congestion.
Who Bloom Bot Is For
- Active on-chain traders who thrive on fast-moving DEX markets and want automation without writing scripts.
- Solana and EVM cross-chain users who want to manage trades, wallets, and triggers under one platform.
- Semi-technical users who appreciate automation but prefer guided UI workflows over command-line complexity.
- Professional copy traders looking for a system that balances speed, control, and customization.
Who It’s Not For
- Institutional or risk-averse users demanding formal audits and open-source verification.
- Data-heavy analysts who rely on complex PnL dashboards and historical charting tools.
- Absolute beginners who might find even simplified automation intimidating without guidance.
Final Evaluation

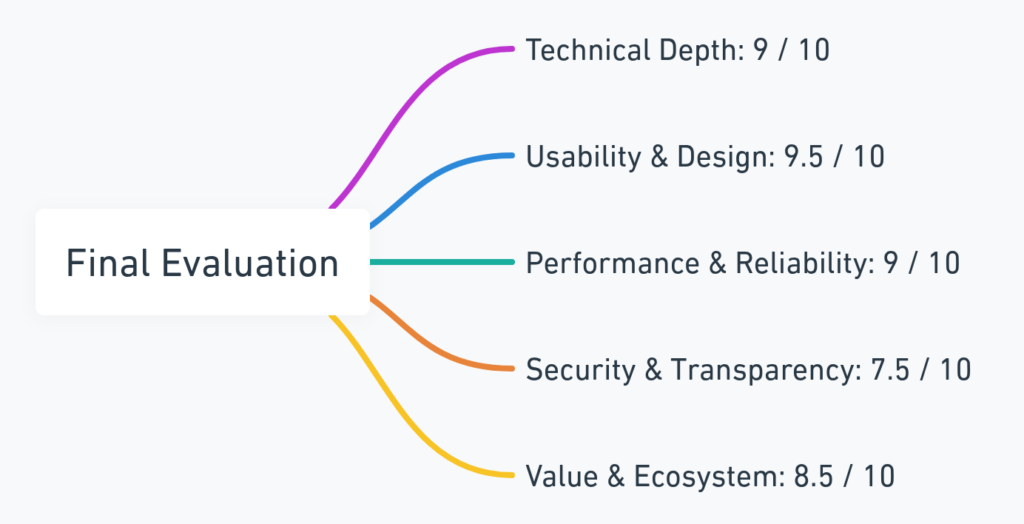
Technical Depth: 9 / 10
Robust modular backend, event-driven architecture, and excellent latency management.
Usability & Design: 9.5 / 10
Intuitive Telegram interface plus an efficient browser extension make it highly approachable.
Performance & Reliability: 9 / 10
Strong across both Solana and EVM, with minimal downtime and solid fill rates.
Security & Transparency: 7.5 / 10
Non-custodial wallet handling is great, but the absence of third-party audits and backend visibility prevents a perfect score.
Value & Ecosystem: 8.5 / 10
Balanced pricing, referral incentives, and an active community create sustainable value.
Overall Rating: 8.9 / 10
Bloom Bot v2.0 is a top-tier multi-chain trading automation platform that stands out for its technical maturity, clean UX, and consistent reliability.
It’s fast enough for snipers, intelligent enough for copy traders, and simple enough for casual users who want professional tools without the friction.
With continued transparency efforts and expanded analytics, Bloom has the potential to become the benchmark for decentralized trading bots in both the Solana and EVM ecosystems.
