How to start Forex Trading from India?
The forex market, also called FX, is like a global money hub that never sleeps, thanks to technology. It lets people trade different currencies 24/7. Imagine it as several markets, like one for the US dollar and another for the British pound. Big financial transactions between banks, called interbank transactions, impact how much each currency is worth. The forex market started to help with international trades and is the oldest financial market, playing a big role in global money flow.
Table of Contents

What is Forex trading?????
Forex trading, or foreign exchange trading, is a dynamic financial activity centered around the buying and selling of currencies on the global market. As the largest and most liquid decentralized market worldwide, Forex presents substantial profit opportunities.
Forex trading is the global marketplace where currencies are bought and sold against one another. Traders engage in this decentralized market to profit from fluctuations in exchange rates. In India, major currency pairs like USD/INR (US Dollar to Indian Rupee) are commonly traded. Participants can speculate on whether a currency will strengthen or weaken, creating profit opportunities.
Regulatory Environment
The regulatory environment for Forex trading in India is governed by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI).
Residents can trade in the Forex market under the Liberalized Remittance Scheme (LRS) of the RBI, which permits individuals to remit up to a certain amount annually for permissible capital and current account transactions, including Forex trading.
Choosing a Reliable Broker
Selecting a trustworthy Forex broker is a critical step for Indian traders. It’s advisable to opt for brokers regulated by international financial authorities, ensuring adherence to global standards. Additionally, considering a broker’s reputation, trading platform, and customer support can provide a seamless trading experience.
This includes providing your credentials and completing the KYC (Know Your Customer) process. In this step, think about the payment options available and choose the one that allows you to easily deposit and withdraw with your preferred broker.
Account Types and Minimum Deposits
- Different brokers offer various account types with varying minimum deposit requirements. Consider your budget and trading preferences to find a broker that aligns with your financial goals. Some brokers provide accounts with no minimum deposit, making them accessible for traders with different capital levels.
Also Read–> Top 3 best JPY/USD Indicators a Trader must use
Leverage and Margin
- Leverage is a key component in Forex trading, allowing traders to control larger positions with relatively little capital. However, excessive leverage can amplify both gains and losses. Choosing a broker that offers suitable leverage options is crucial based on your risk tolerance and trading strategy.
Trading Instruments
- While major currency pairs are universally offered, the availability of other financial instruments like commodities, indices, and cryptocurrencies may vary among brokers. Choose a broker that provides access to the markets and assets you are interested in trading.
Open a Trading Account
Once you’ve chosen a broker, you’ll need to open a trading account.
This typically involves providing personal information KYC (Know Your Customer), completing verification processes, and funding your account.
Be sure to start with a demo account if the broker offers one, allowing you to practice trading in a risk-free environment.
Risk Management

Forex trading involves inherent risks, and Indian traders must implement effective risk management strategies. This includes setting stop-loss orders, diversifying portfolios, and avoiding overleveraging positions. Educating oneself about market trends and staying informed about global economic factors is also essential.
You may Also Read –> Understanding Risk-Reward Ratios
Setting Stop-Loss Orders
One fundamental pillar of risk management in Forex trading is the prudent use of stop-loss orders. These orders act as a safeguard, allowing traders to define a predetermined point at which a losing position will be automatically closed. By setting stop-loss orders, Indian traders can mitigate potential losses and maintain a disciplined approach to risk.
To know more about Stop-Loss READ- Stop-loss Simplified: Guarding Your Investments With Ease
Diversifying Portfolios
Diversification is a time-tested risk management technique that involves spreading investments across different assets or currency pairs.
This strategy aims to reduce exposure to a single market or currency, minimizing the impact of adverse movements in any particular segment.
By diversifying portfolios, traders in India can enhance the resilience of their overall investment strategy.
Avoiding Overleveraging
The allure of leverage in Forex trading is undeniable, offering the potential for amplified profits. However, it is equally crucial to recognize the risks associated with overleveraging.
Indian traders should approach leverage with caution, using it judiciously and aligning it with their risk tolerance. Overleveraging positions can magnify losses, underscoring the significance of adopting a balanced and measured approach.
Tax Implications

Indian traders engaging in Forex activities must be aware of the tax implications. Forex gains are subject to capital gains tax, and it’s advisable to maintain detailed records of transactions for tax reporting purposes.
Seeking guidance from tax professionals can help ensure compliance with Indian tax laws.
Capital Gains Tax Considerations
Forex gains fall within the purview of capital gains tax in India. The classification of gains into short-term or long-term is contingent on the holding period of the traded currency pairs.
Short-term capital gains (STCG) arise from holdings with a tenure of less than 36 months, while Long-term capital gains (LTCG) are associated with assets that stay longer than 36 months.
As per the prevailing tax laws, short-term capital gains are subject to the applicable income tax slab rates, while long-term capital gains on listed securities incur a fixed rate of 10%, without indexation benefits.
Also Read–> Crypto Chart Pattern Cheat Sheet
Detailed Record Keeping
Maintaining meticulous records of Forex transactions is a cornerstone of effective tax management.
These records should encompass a comprehensive overview of all trades, profits, losses, and associated expenses.
The importance of organized record-keeping cannot be overstated, as it not only facilitates accurate gain or loss calculations but also serves as a foundational component during the preparation of tax returns.
Tax Deductions and Eligible Expenses
Indian traders engaging in Forex activities may be eligible for certain tax deductions related to their trading endeavors.
Deductions may extend to expenses directly linked to trading, such as platform fees, data subscriptions, and internet costs.
Consulting with tax professionals becomes crucial to ascertain the specific deductions applicable to an individual trader’s circumstances, ensuring that eligible expenses are appropriately considered in the tax planning process.
Trading styles
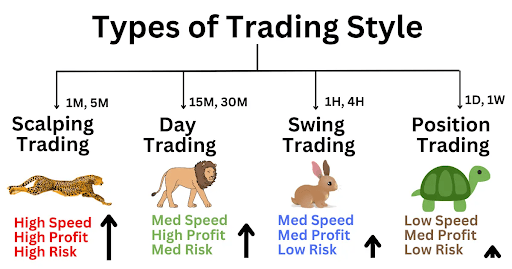
1. Day Trading
Day trading is like a quick game of buying and selling assets in the financial world, all in one day. Imagine you’re trying to make money by taking advantage of prices going up and down fast.
Day traders watch the market closely, make speedy decisions, and aim to finish all their buying and selling before the day is over.
Being good at day trading means being fast, managing risks smartly, and understanding how prices move in the market.
To know more about Day Trading Read- Top Crypto Day Trading Indicators!
2. Swing Trading
Swing trading is a style of trading where investors hold onto their positions for a few days to weeks, taking advantage of short to medium-term market trends. Unlike day trading, swing traders don’t need to make decisions within a single day.
Successful swing trading involves analyzing trends, and patterns, and using both technical and fundamental analysis to make informed decisions about when to enter and exit trades.
To know more about Swing Trading Read–> Mastering Crypto Swing Trading Strategies for Maximum Profits – A Comprehensive Guide
3. Position Trading
Position trading is a patient and long-term approach to trading financial assets. Unlike day or swing trading, position traders take a much broader view, holding positions for weeks, months, or even years.
The goal is to benefit from major market trends and economic cycles. Position traders rely heavily on fundamental analysis, considering factors like economic indicators, financial reports, and overall market conditions.
Successful position trading involves strategic entry and exit points based on a comprehensive understanding of the market’s long-term trajectory.
4. Scalping
Scalping is a rapid-fire style of trading in the financial markets. Traders employing this strategy aim to make quick, small trades to exploit minor price fluctuations. Unlike other trading styles, scalping is all about speed, with positions being held for a very short time—sometimes just seconds or minutes.
Successful scalping relies on leveraging small price movements for incremental gains, making it suitable for those who thrive in fast-paced and dynamic trading environments.
Forex Terminologies
1. Pip and Spread
Delving into the basics, a “pip,” which stands for “percentage in point,” represents the smallest possible price movement in a currency pair. It’s the incremental change, akin to the tiniest step a currency can take.
Moving on, the “spread” is the dynamic gap existing between the bid (buying) and ask (selling) prices of a currency pair, effectively encapsulating the transaction costs involved.
2. Long and Short Positions
Trading in the forex market involves strategic decisions regarding positions. Going “long” denotes the act of purchasing a currency pair with the anticipation that its value will ascend.
Conversely, adopting a “short” position involves selling a currency pair with the expectation that its value will decline.
3. Leverage and Risk Management
The concept of “leverage” introduces a layer of complexity to forex trading, allowing traders to control positions that exceed their capital. While this can magnify potential profits, it concurrently elevates the risk of substantial losses.
Therefore, implementing robust “risk management” strategies becomes imperative. Tools such as “stop-loss” orders serve as safeguards by automatically closing a position when a predetermined price level is reached, limiting potential losses. On the flip side, “take profit” orders secure gains at specified levels, ensuring a balanced approach to risk and reward.
4. Currency Pairs
Currencies in the forex market are paired together, each reflecting a unique relationship. For instance, in the EUR/USD pair, the Euro is the “base currency,” and the US Dollar is the “quote currency.”
These pairs are broadly categorized into “major,” “minor,” and “exotic,” each carrying its significance and liquidity in the vast forex landscape.
5. Market and Limit Orders
Executing trades in the forex market involves the strategic use of orders. A “market order” allows traders to buy or sell a currency pair at the current market price, facilitating immediate transactions.
On the other hand, a “limit order” empowers traders to set specific entry points at more favorable prices than the prevailing market rate, injecting a layer of precision into their trading strategies.
6. Overnight Game – Rollover/Swap
The Forex game doesn’t pause when the sun sets. “Rollover” or “swap” comes into play when positions are held overnight. Traders may either earn or pay interest, and this is determined by the interest rate differential between the two currencies in the pair.
Make a profit with Forex
When it comes to making money with Forex in India, the challenge lies in the limited variety of foreign currencies available for trading. Indian residents are restricted to forex pairs that include the Indian Rupee (INR). However, a noteworthy and popular currency pair is the USD/INR, which offers an appealing return rate.
USD/INR Currency Pair
Historically, the USD has demonstrated a consistent trend of strengthening over the years. An especially promising forex pair is USD/INR. Analyzing its recent performance reveals a 52-week low of 68.2900 and a 52-week high of 76.9163. This substantial range presents traders with a lucrative opportunity to leverage price movements for significant profits in both short and long-term trading.
Forex trading at a glance in India
Forex trading in India can be a rewarding venture with some important steps to keep in mind. It’s crucial to learn continuously, manage risks wisely, and understand different trading styles, from quick day trading to patient position trading.
Choosing a trustworthy broker and being aware of regulatory guidelines are key to a smooth trading experience. Tax implications should be considered, and it’s beneficial to keep detailed records of transactions.
Even though there are limited foreign currencies for Indian traders, the USD/INR pair stands out as a good option due to its historical performance and profit potential. Remember, success in Forex comes with ongoing learning, smart decision-making, and adapting to the ever-changing market. Happy trading!
FAQ
What is Forex trading?
Forex trading, or foreign exchange trading, involves the buying and selling of currencies on the global market. It’s the largest and most liquid market worldwide, where traders aim to profit from changes in currency exchange rates.
How can I start Forex trading in India?
To start Forex trading in India, educate yourself on market basics, choose a reliable broker regulated by authorities like RBI and SEBI, open a trading account, and practice with a demo account. Be aware of the regulatory environment and tax implications.
What is the significance of the USD/INR currency pair?
The USD/INR currency pair involves the US Dollar and the Indian Rupee. It’s crucial for Indian traders as it allows speculation on the exchange rate between these two currencies. Its historical performance and attractive return rate make it popular among traders in India.
How can I manage risks in Forex trading?
Effective risk management in Forex includes setting stop-loss orders, diversifying portfolios, and avoiding overleveraging. These strategies help protect your capital and maintain a disciplined approach to trading.
Are there tax implications for Forex traders in India?
Yes, Forex gains in India are subject to capital gains tax. Traders should maintain detailed records of transactions for tax reporting purposes. Consultation with tax professionals is advisable to understand deductions and ensure compliance with tax laws.
