Derp.trade Review: Leverage Any Asset
Derp.trade is an on-chain perpetuals protocol built around “DERPs”, a derivative primitive designed to let traders go long or short with leverage even on assets that normally lack deep liquidity. Instead of relying on an order book, it uses an AMM-based design and protocol-level risk controls to keep markets tradable, with documentation focused on how pricing, margin, liquidation, and pool safety mechanisms work under the hood. Read this Derp.trade Review to know more about the platform.
What is Derp.trade?
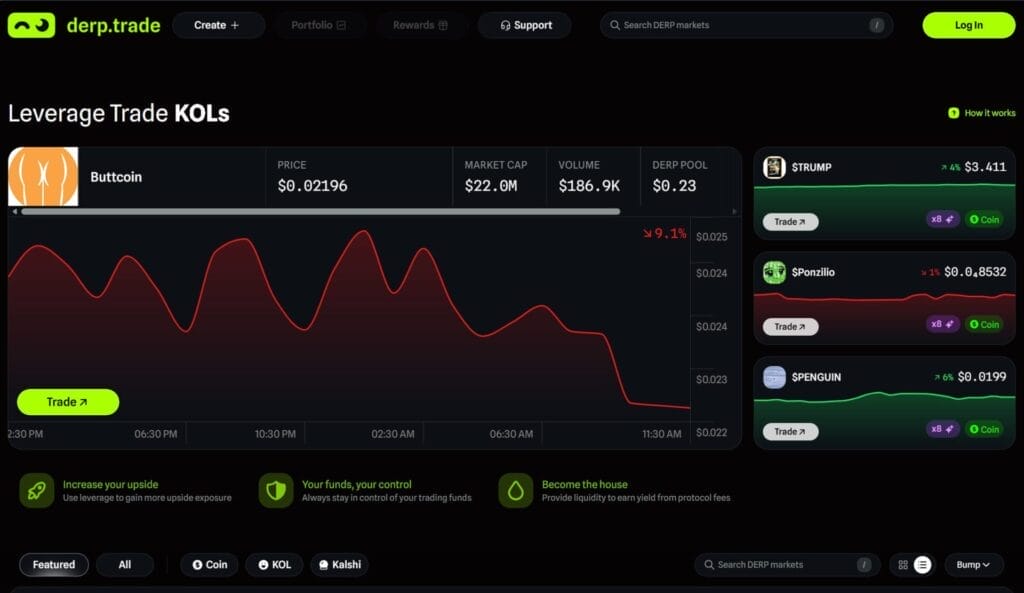
Derp.trade is a Solana-based derivatives DEX built around DERPs (Decentralized Perpetuals). The core pitch is simple: create and trade leveraged long or short markets for practically any on-chain asset, even when that asset has low volume or thin liquidity.
What makes DERPs different from classic perps
Most perp venues depend on deep liquidity (often via order books or heavy LP programs). Derp.trade instead uses an AMM-first design, and it focuses on controlling market skew (imbalance between total long and short exposure). Skew is used to influence pricing and funding, so the market can stay functional even when one side dominates.
Also, you may read Hyperliquid vs Pacifica vs Reya vs EdgeX vs Orderly
Derp.trade Review: Key Features
- Leverage “any asset” goal: designed to support a wide set of underlyings (tokens, and in concept even equities or commodities as markets) without needing high baseline liquidity.
- AMM pricing + funding driven by skew: prices and funding rates adjust based on long vs short imbalance, not just traditional funding mechanics.
- AMM cannot be liquidated: liquidations apply to traders’ positions, but the AMM is treated as a special counterparty.
- Payout clamp when liquidity is insufficient: if the AMM cannot fully cover unrealized PnL, withdrawals can be limited to available AMM liquidity (this is a key “risk model” difference versus many perp systems).
- Dynamic max leverage target: docs describe leverage aiming to move between 1x and 100x depending on market conditions (with current limits tighter while in development).
- SDK for integrators and bots:
@derp-trade/sdkexists for programmatic order creation and integration into terminals or automation
Also, you may read Top AsterDEX Alternatives
Derp.trade Review: Asset Specifications
| Characteristic | Perpetual futures (Hyperliquid) | DERPs |
|---|---|---|
| Contract | Unit of underlying spot asset | Unit of underlying spot asset |
| Underlying asset | Any asset via price oracle | Any asset via price oracle or direct spot price retrieval |
| Initial margin fraction | 1 / leverage | Maintenance margin + max half-spread increase + max funding rate between liquidation checks + size-dependent risk buffer |
| Maintenance margin | 0.5 * max initial margin | Pre-set base rate + debt sensitivity * AMM debt ratio |
| Mark price | Robust, order book-based | Robust, based on AMM mid-price |
| Account type | Cross or isolated margin | Isolated margin |
| Funding rate | Based on index and mark price difference | Based on market skew |
Also, you may read Apex Trader Funding Review
Derp.trade Review: Fees
Derp.trade charges a flat 60 bps (0.6%) fee per order, calculated on the notional value of the trade. That means the fee is applied to the full trade value, not your leverage multiple or just your margin amount.
Fee split
- 30 bps liquidity fee: routed directly into AMM liquidity
- 30 bps platform fee: retained by the platform
- Referral program: lets inviters earn a portion of the platform fee paid by their referrals
Also, you may read TOP 5 Axie Infinity Staking Platforms: Earn Massive Rewards
When and how it’s charged
- Fees are charged in USD
- Deducted:
- on open: from the funds used to open the position
- on close: from sale proceeds
- Not charged on:
- unrealized PnL
- Not included in:
- account value calculation
Discounts and rebates
- No rebates or volume discounts currently
- The docs note this may change later
Also, you may read Top 10 PolyMarket Analytics Tools
Quick fee table (simple)
| Fee Item | Rate | Applied On | Where it goes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total trading fee | 60 bps (0.6%) | Notional per order | Split below |
| Liquidity fee | 30 bps (0.3%) | Notional per order | Added to AMM liquidity |
| Platform fee | 30 bps (0.3%) | Notional per order | Platform (shareable via referrals) |
Derp.trade Review: AMM
DERPs on derp.trade are not matched through an order book. Every trade executes against an automated market maker (AMM), meaning the protocol itself is the counterparty and the pricing logic lives on-chain inside a smart contract.
How pricing works
Instead of using a constant-product curve (like classic CPMMs), derp.trade’s AMM sets the DERP price using two inputs:
- the underlying asset price, and
- the AMM’s debt / skew state (how imbalanced longs vs shorts are).
So pricing is not “pool ratio math,” it is a risk-aware quote that shifts based on market imbalance.
Also, you may read 8 Best Crypto Ad Network
Order types without an order book
Even without an order book, derp.trade still supports multiple order types. The key behavior is:
- Orders can sit and wait until their conditions trigger
- Once triggered, they execute at the current AMM price
- There is no guarantee you get your exact intended price, because the AMM price may have moved by the time execution happens
What this means in practice
- You get always-on execution access (no need for active makers)
- But you trade with AMM price risk, especially in thin or skewed markets
- Limit-style orders behave more like “conditional orders” that fill when the trigger is hit, not like “guaranteed maker quotes” on a deep book
Also, you may read Hyperliquid vs Orderly vs Avantis vs Reya vs Based
Derp.trade Review: Order Types
derp.trade aims to support three types of orders: market, limit, and stop market orders.
Market orders execute immediately at the market price. Limit orders execute at a specified price or better, and they will remain open until filled or cancelled.
Stop market orders are triggered when the market price reaches a specified level, and they execute as market orders – they are not guaranteed to fill at the stop price. They are used to implement stop loss and take profit.
The current version of the app only supports market orders. Limit and stop market orders are planned for future releases.
Also, you may read EdgeX vs Pacifica vs Extended vs AsterDEX vs Hyperliquid – Check NOW!
Derp.trade Review: Margin
Derp.trade uses margin to decide how much collateral you must post to open a leveraged position and how much you must keep to avoid liquidation. The big design choice is that derp.trade supports isolated margin only, so every position has its own collateral bucket and is liquidated independently.
Isolated margin only
- Each position has separate margin
- You deposit and withdraw per order
- Liquidations happen per position, not across your whole account
This reduces cross-position contagion, but it is less capital-efficient than cross margin.
Leverage mechanics
Maximum leverage is market-dependent. The protocol targets a dynamic max leverage that can move between 1x and 100x, based on:
- available liquidity
- AMM skew
In practice, leverage limits are currently constrained during development and intended to increase over time.
Also, you may read Cypher Card Review: Spend your crypto like Cash
Initial margin (opening a position)
To open a position, your deposit to the market-specific account must exceed the initial margin. The key idea:
- Deposit equal to initial margin means you are effectively using max leverage
- Lower leverage requires extra collateral
Also, you may read Binance NFT Loan Service: Get Loans on Bored Ape
How initial margin rate is built
Derp.trade starts from the maintenance margin rate and adds three buffers:
- Spread-widen buffer
Adds half of the maximum quote deviation expected before the next liquidation check. - Funding-accrual buffer
Covers worst-case funding debt that could accrue before the next liquidation check. - Size buffer (risk tiers)
As position size increases through predefined steps, initial margin increases.
This is the core “illiquidity-first” design. Bigger positions and more volatile conditions require more upfront safety collateral.
Also, you may read Zona Review: Lending and Borrowing Infrastructure
Derp.trade Review: Liquidation
Derp.trade liquidates a position when the position value + deposited collateral drops below the maintenance margin. The stated goal is protocol solvency and preventing the AMM from becoming undercollateralized.
Automatic, protocol-executed liquidations
- Liquidations are executed automatically by the protocol
- The system monitors user account value in real time
- When maintenance margin fails, the protocol closes the position against the AMM
The harsh part: liquidation forfeits all collateral
Derp.trade’s liquidation policy is explicit:
- After liquidation, users do not receive any remaining collateral
- Liquidation results in loss of all funds deposited as collateral for that isolated position
In review language: liquidation is not a “close position and return leftover margin” model. It is a full collateral wipe for the liquidated position.
Also, you may read What Is Rate-X? A Complete Guide to the First Leveraged Yield Exchange
Derp.trade Review: Preventing Drain Attacks
Perps markets require a market maker, which uses a pool of its own funds to provide liquidity. This means that exploiting one market can cause the market maker to lose money used to provide liquidity in other markets.
This is a concern for perps exchanges, but not for derp.trade, because:
- All DERPs pools are independent. One pool’s liquidity cannot be used to cover another pool’s losses.
- There is no socialized insurance fund. Instead, each pool is separately overcapitalized.
- The AMM cannot be liquidated, instead using the real value mechanism to limit the amount of funds that can be drained from the AMM.
Also, you may read ORO Finance Review: A New Infrastructure for Digital Gold
Conclusion
Derp.trade is built for a very specific promise: leverage on any on-chain asset without needing deep order-book liquidity. It delivers that through an AMM-priced perp design where skew and AMM debt directly shape pricing, funding, and margin requirements. The tradeoff is clear in the docs: risk controls are conservative, and liquidation is strict. If you want access and composability (SDK, on-chain markets, isolated positions), derp.trade is compelling. If you want softer liquidation outcomes or guaranteed limit fills, the protocol’s mechanics demand extra caution.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are DERPs?
DERPs are decentralized perpetual futures built to work even when the underlying market is illiquid. They use an AMM instead of an order book and rely on skew-based mechanics to manage risk.
Is margin cross or isolated?
Derp.trade supports isolated margin only. Each position has separate collateral and is liquidated independently.
Do I get remaining collateral back after liquidation?
No. The docs state that after liquidation, users do not receive any remaining collateral, meaning liquidation results in loss of the collateral deposited for that position.
